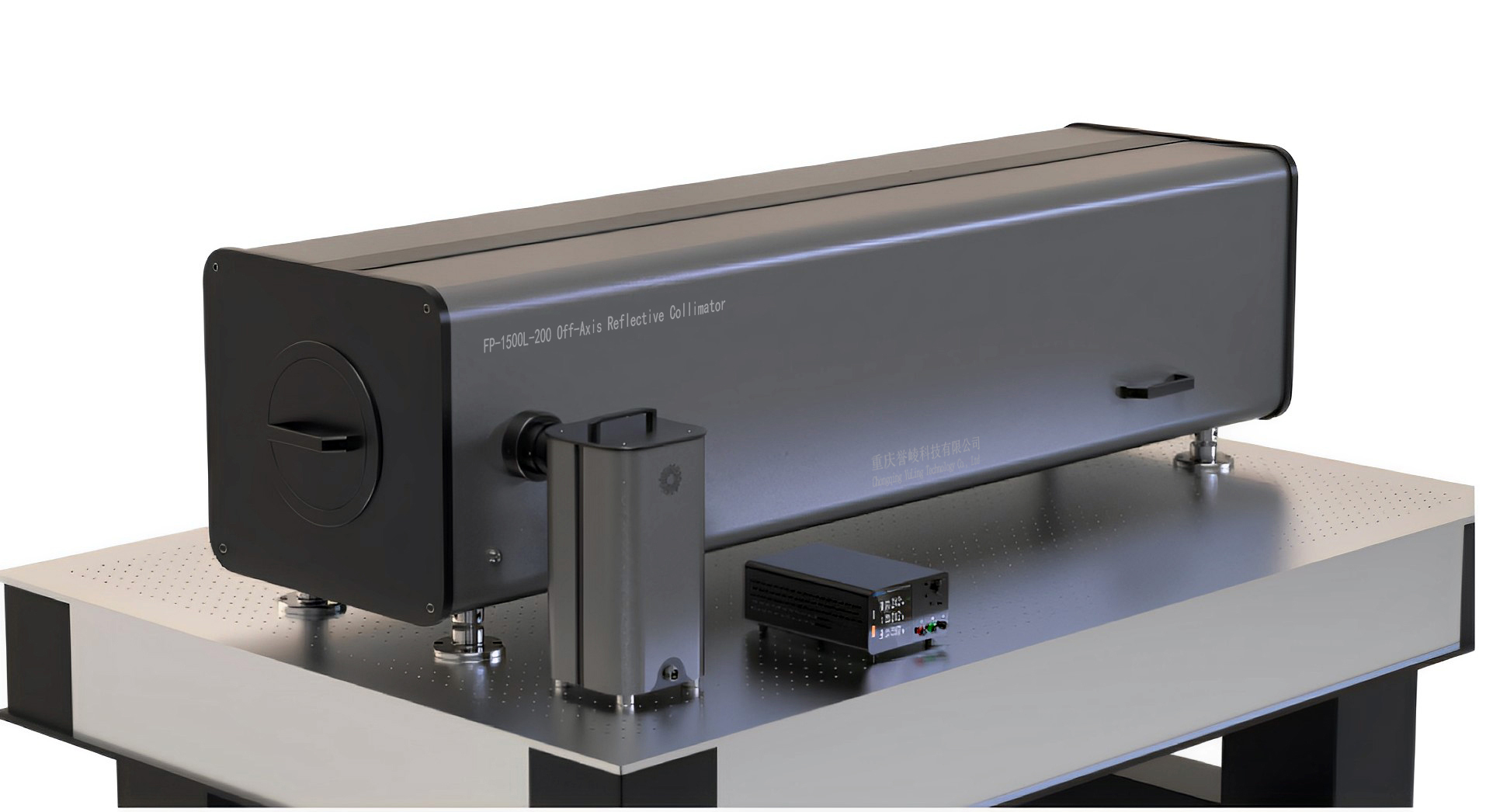
Off-Axis Optical Structure And Design
The FP-1500L-200 Off-Axis Parabolic Collimator generates high-quality parallel beams through its off-axis mirror configuration, ensuring an unobstructed ϕ200 mm clear aperture. By separating the primary and secondary mirrors, it eliminates optical path interference and secondary reflections, maintaining ≤5″ beam parallelism and RMS ≤ 1/40λ @ 632.8 nm precision. The design delivers ultra-low divergence parallel light for optical axis calibration, infinite-target simulation, and imaging system testing across multi-wavelength applications including visible, infrared, and laser systems.
Precision Reflective System And Lens Collimator Performance
The optical system uses a quartz-glass primary mirror with aluminum + Si coating (optional gold, silver, or dielectric). Its lens collimator characteristics include a 1500 mm focal length (±1%), field of view ≥ 1.07°, and reflectivity ≥ 85%. Wavefront aberration RMS ≥ 1/15λ ensures stability in long-term use. The secondary planar mirror redirects the optical path to the instrument’s side for convenient adjustment, while the modular focal plane allows interchangeable reticle plates for resolution and alignment analysis.
Modular Configuration And Testing Capabilities
This rectangular collimator system includes a halogen light source, filters (600 nm & 532 nm), and 12 visible reticles (crosshair, USAF 1951, star-point, and resolution types). Infrared targets—such as four-bar, circular, and slit plates—enable MRTD, MDTD, and SRF testing using a blackbody source. Additional targets for distortion, outline, and NETD evaluation expand functionality for thermal imaging and camera calibration. The flexible structure supports rapid module replacement for efficient metrology, laboratory validation, and aerospace optical testing.
Key Functions:
- Optical axis alignment for multi-axis systems in visible, infrared, and laser wavelengths.
- Basic parameter testing of optical systems using various reticles and additional accessories.
- Infrared imaging quality testing and optical axis alignment with a blackbody source.
- Laser beam expansion by integrating with a laser source.
- Provides ultra-low divergence angle parallel light.
- Simulates an infinite target.
Optical path diagram:
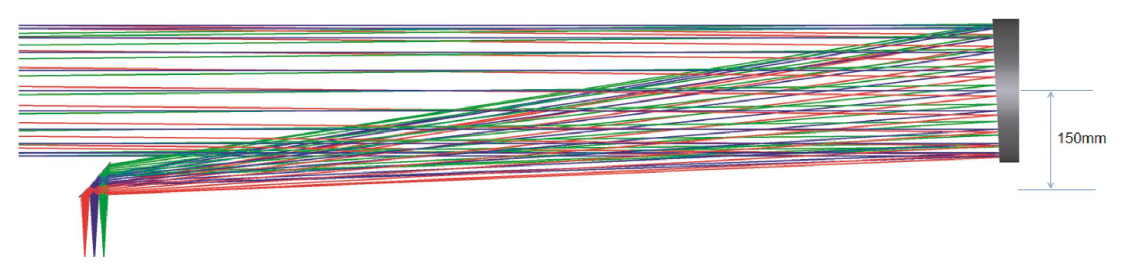
- The main reflector adopts an off-axis surface mirror, select the appropriate off-axis, so that the reflected optical path deviates from the optical axis, avoids the secondary reflector from interfering with the light-passing optical path, and ensure that the φ200mm light-permeable area is unobstructed.
- The secondary mirror adopts a plane reflector, which undertakes the reflected light path of the main reflector and turns the light path, so that the reflected light path is located on the side of the light outlet, which is convenient for later debugging and use.
- The focal plane position is the target surface installation position. Each target plate is installed in the dividing plate frame separately. Through later debugging, each target plate is placed in the focal surface position after separate assembly to realize the target plate replacement function.
Standard Components:
- Collimator Main Unit: 1 set
- Filters: 2 pieces (Orange, center wavelength 600nm; Green, center wavelength 532nm)
- Attenuator: 1 piece (Neutral Attenuator 430–730nm)
- Visible Reticles: 12 pieces(Crosshair Reticles*1,Resolution Reticles*5:1#/2#/3#/4#/5#,Star Point Reticles*5: 0.1/0.2/0.01/0.02/0.05,Porro Board*1)
- USAF 1951 Resolution Reticle: 1 piece
- Light Source Assembly: 1 set( 12V30W Halogen Light Source)
Custom Components (Applicable to Infrared Reticles):
Infrared targets are formed by machining various patterns into thin metal plates. When illuminated by a blackbody source, the thermal imager under test observes sharp target patterns against a uniform background. A variety of standard infrared targets are available for customization.
Examples of Targets:
- Four-Bar Target: For Minimum Resolvable Temperature Difference (MRTD) testing.
- Circular Target: For Minimum Detectable Temperature Difference (MDTD) testing.
- Slit Target: For Slit Response Function (SRF) testing.
- Cross-Circle Target: For axis alignment, aiming, and focusing.
- Distortion Target: For testing camera distortion in image generation.
- Outline Target: For evaluating target recognition range of the camera under test.
- Square Target: For testing Noise Equivalent Temperature Difference (NETD), Fixed Pattern Noise (FPN), Signal Transfer Function (SITF), and Aperiodic Transfer Function (ATF).
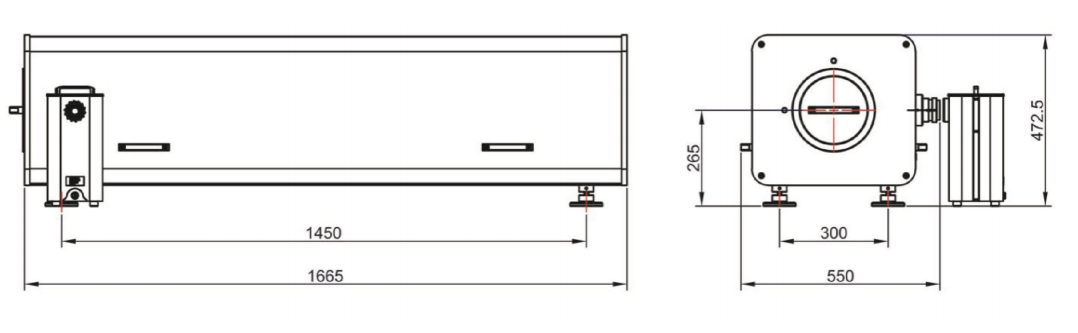
External dimensions:(Unit: mm)
About Us
YuLing Technology, headquartered in Chongqing, China, is a specialized manufacturer of optical and photoelectric instruments. Its R&D center in Xi’an focuses on the design and production of collimators, autocollimators, optical benches, and metrology systems for aerospace, defense, and precision industry sectors. The company combines optical design, mechanical manufacturing, and control system integration to deliver high-accuracy calibration tools. YuLing emphasizes quality assurance, engineering precision, and technical support, providing reliable, custom-tailored optical solutions that meet international performance standards.
Request detailed specifications or discuss your optical calibration needs with YuLing today!
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions
What precision does the FP-1500L-200 Parabolic Collimator achieve?
It provides ≤5″ beam parallelism and RMS ≤ 1/40λ @ 632.8 nm verified through interferometric testing.
What wavelength range can the system operate in?
It supports visible (380–780 nm), infrared, and laser wavelengths for multi-domain calibration.
Can the mirror coatings be customized?
Yes, aluminum + Si is standard, with optional gold, silver, or dielectric coatings based on spectral requirements.
Is the rectangular collimator system modular?
Yes, interchangeable reticles and infrared targets allow users to perform MRTD, SRF, and alignment tests efficiently.
What is the lead time for production?
Standard manufacturing and inspection take 4–6 weeks depending on customization options and accessory configurations.

