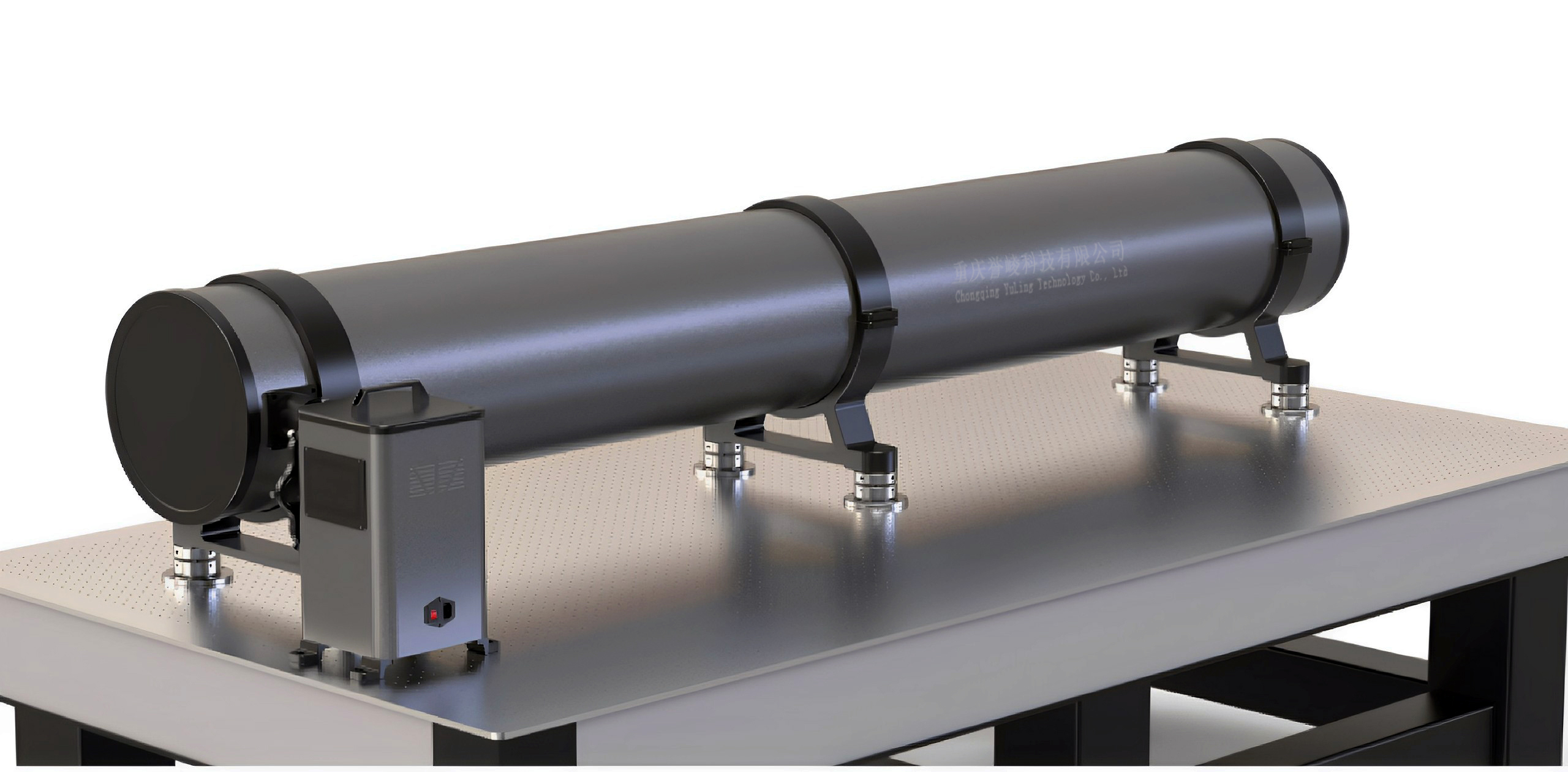
Introduction:
The coaxial reflective collimator is primarily used as an optical instrument for optical axis alignment. This instrument features a large aperture and wide spectral range, making it ideal for multi-axis alignment of optical systems, including laser, television, and visual optical axes. When equipped with additional accessories, it can also measure other optical system parameters.(The disadvantage is that there is an obstruction in the center.)
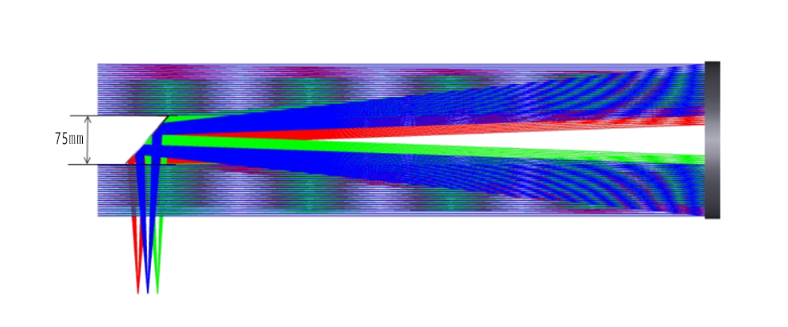
Optical path diagram:
Standard Components:
- Collimator Main Unit: 1 set
- Filters: 2 pieces (Orange, center wavelength 600nm; Green, center wavelength 532nm)
- Attenuator: 1 piece (Neutral Attenuator 430–730nm)
- Visible Reticles: 12 pieces(Crosshair Reticles*1,Resolution Reticles*5:1#/2#/3#/4#/5#,Star Point Reticles*5: 0.1/0.2/0.01/0.02/0.05,Porro Board*1)
- USAF 1951 Resolution Reticle: 1 piece
- Light Source Assembly: 1 set( 12V30W Halogen Light Source)
Custom Components (Applicable to Infrared Reticles):
Infrared targets are formed by machining various patterns into thin metal plates. When illuminated by a blackbody source, the thermal imager under test observes sharp target patterns against a uniform background. A variety of standard infrared targets are available for customization.
Examples of Targets:
- Four-Bar Target: For Minimum Resolvable Temperature Difference (MRTD) testing.
- Circular Target: For Minimum Detectable Temperature Difference (MDTD) testing.
- Slit Target: For Slit Response Function (SRF) testing.
- Cross-Circle Target: For axis alignment, aiming, and focusing.
- Distortion Target: For testing camera distortion in image generation.
- Outline Target: For evaluating target recognition range of the camera under test.
- Square Target: For testing Noise Equivalent Temperature Difference (NETD), Fixed Pattern Noise (FPN), Signal Transfer Function (SITF), and Aperiodic Transfer Function (ATF).
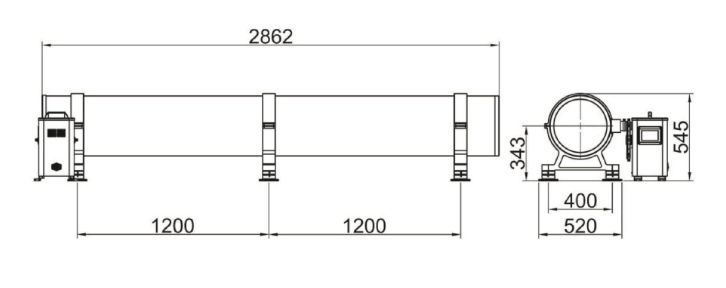
External dimensions:(Unit: mm)